What is a Curriculum Vitae (CV)?
A Curriculum Vitae (CV) is a comprehensive document that provides a detailed overview of a person’s academic and professional history. It’s a thorough record, often used in academic, research, and international job applications. Unlike a resume, a CV presents a complete account of your qualifications, achievements, and experiences. It’s designed to provide a full picture of your professional journey, including everything from education and publications to grants and awards. The CV serves as a primary document, giving potential employers or institutions a complete overview of your skills and expertise in your field. Understanding what constitutes a CV is critical for anyone aiming for opportunities where a deep dive into their professional history is expected. It is also the basic document.
Key Components of a CV
A strong CV typically includes several key components to showcase your qualifications effectively. The most common sections are contact information, education, work experience, skills, and additional sections tailored to your field. These additional sections can include publications, presentations, grants, awards, and professional affiliations. Each part plays a crucial role in presenting a well-rounded view of your background and capabilities. By strategically arranging these elements, you can create a CV that highlights your most relevant achievements and skills, which can be very useful to gain an edge.
Education and Qualifications

The education section of a CV should include all your academic achievements. Start with the most recent degree first, listing the degree earned, the name of the institution, the dates of attendance, and any honors or awards. You may also include your thesis or dissertation title, and any relevant coursework that aligns with the job or opportunity you’re seeking. Highlighting your educational background properly is a significant part of a compelling CV, demonstrating your commitment to learning and expanding your expertise.
Work Experience
The work experience section should detail your professional background. Include the job title, the name of the organization, the dates of employment, and a description of your responsibilities and accomplishments. Use action verbs to describe your tasks and quantify your achievements whenever possible. This section provides insight into your practical skills and how you’ve applied your knowledge in real-world scenarios. Including specific examples will help to highlight your abilities and your impact.
Skills and Achievements
Include a separate section for your skills and achievements. This can include technical skills, language proficiency, and other relevant abilities. Also, list any awards, publications, presentations, or projects that demonstrate your expertise and accomplishments. Highlighting your skills and achievements enables potential employers or institutions to quickly identify your strengths and contributions, making it a key element of a successful CV. Always align your skills with the job’s requirements.
Publications and Presentations
If applicable, dedicate a section to publications and presentations. List all your published work, including the title, journal or conference, and publication date. For presentations, include the title, location, and date. These details demonstrate your contributions to your field and your ability to share your knowledge with others. This is particularly important for those applying for academic or research positions. It will show your expertise.
What is a Cover Letter?
A cover letter is a concise document that accompanies your resume or CV when applying for a job. It serves as an introduction and a tool to highlight your relevant skills, experiences, and achievements, and to explain why you’re a perfect fit for the specific position. Unlike a CV, which is more comprehensive, the cover letter is tailored to each job application, emphasizing the aspects of your background that best match the employer’s needs. This document gives you a chance to make a personal connection with the hiring manager and present your unique value proposition. It is an essential document for most employers.
Key Components of a Cover Letter
A cover letter typically includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction should state the position you are applying for and how you learned about it. The body paragraphs highlight your relevant skills and experiences, connecting them to the job requirements. The conclusion should reiterate your interest and express your enthusiasm for the opportunity. Each part is critical to making a good impression on the hiring managers. A well-structured cover letter showcases your writing ability and your genuine interest in the role.
Format and Structure

The format of a cover letter should be professional and easy to read. Use a standard business letter format, including your contact information, the date, the employer’s contact information, a salutation (e.g., Dear Mr./Ms. Last Name), the body paragraphs, a closing (e.g., Sincerely), and your signature. Keep the letter concise, ideally no more than one page. Pay attention to the formatting, including margins, font, and spacing, to ensure your cover letter is visually appealing and easy to navigate. Proper formatting demonstrates your attention to detail.
Purpose and Tone
The purpose of a cover letter is to persuade the employer to read your resume and consider you for an interview. The tone should be professional yet personal, showcasing your personality and enthusiasm for the role. Use a tone that is engaging and enthusiastic, conveying your interest in the company and the position. Tailor the tone to match the company culture, while still maintaining a professional demeanor. Your goal is to showcase your value to the employer.
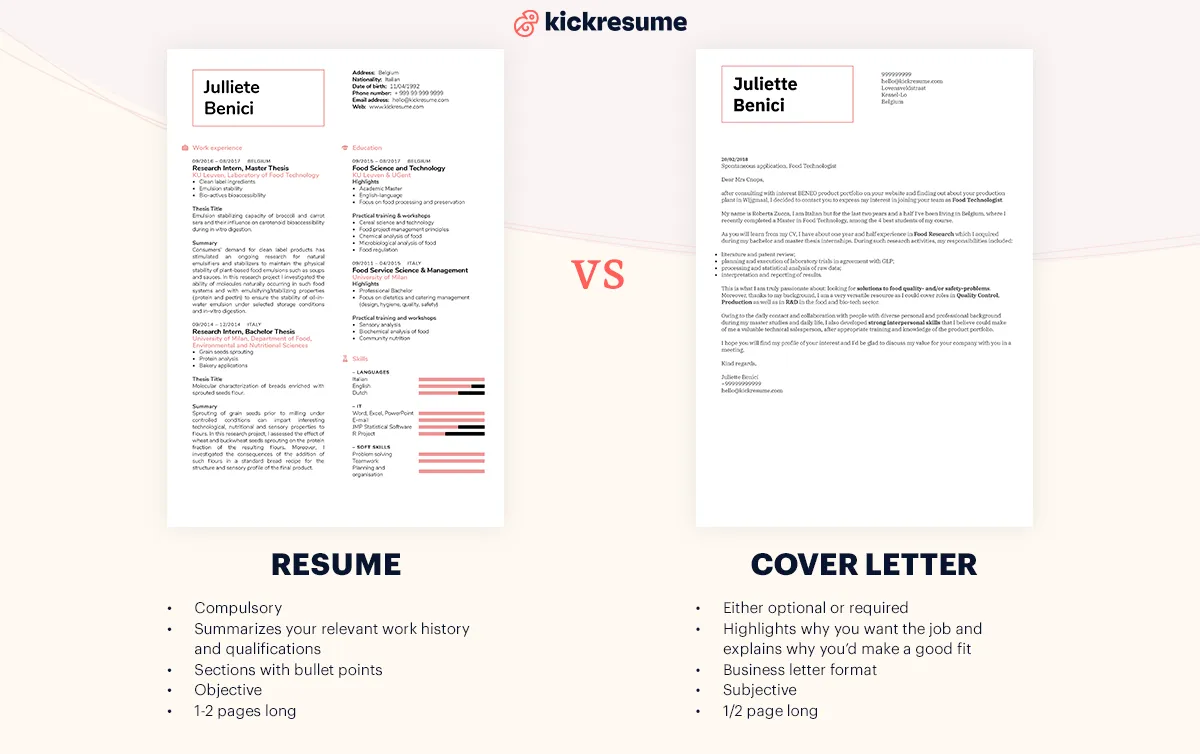
5 Key Differences between a CV and a Cover Letter
Purpose and Scope

A CV is a comprehensive document that provides a detailed account of your academic and professional history, while a cover letter is a concise introduction tailored to a specific job application. The CV is designed to be exhaustive, including all relevant experiences, whereas a cover letter is focused on highlighting your most relevant skills and experiences for the specific role. Knowing the differences in scope will help you utilize each document correctly.
Length and Detail
A CV is generally longer and more detailed, often spanning multiple pages, as it includes a comprehensive record of your qualifications and achievements. A cover letter is usually one page, designed to be brief and to the point, focusing on the most relevant aspects of your experience. The difference in length underscores the distinct purposes of each document, with the CV providing a full history and the cover letter focusing on the job application.
Target Audience
A CV is often used in academic and research settings, or for international job applications, where a detailed account of your background is essential. A cover letter is primarily used for job applications in the United States and other countries where employers prefer a personalized introduction that highlights your fit for a specific role. Understanding the target audience dictates how each document is tailored, based on the employer.
Focus and Emphasis

A CV emphasizes your entire academic and professional history, including all publications, presentations, and research experience. A cover letter focuses on the specific skills and experiences most relevant to the job you are applying for, tailored to match the job description. The emphasis in a cover letter is on demonstrating how your qualifications align with the employer’s needs. The CV provides a broader scope.
Use Cases
A CV is typically used for academic positions, research roles, and international job applications. In these cases, a full record of your qualifications is expected. A cover letter is used for most job applications in the US and other countries, particularly for positions where the employer wants a personalized introduction that highlights your fit for the role. Understanding where to use each one is important. Both the CV and Cover Letter play their specific roles for a job application.
When to Use a CV
A CV is most appropriate for academic positions, research roles, and international job applications. It’s expected in these settings, offering a full picture of your qualifications, including your education, publications, and research experience. Always check the job application instructions to determine whether a CV is required. The CV is your ticket to show the employer how much you know.
Academic and Research Positions

For academic and research positions, a CV is the standard document. Employers will want to see your education, research projects, publications, grants, and any presentations you’ve given. The CV provides a complete view of your academic accomplishments and your contributions to your field. Your work experiences, skills, and achievements are shown in detail here.
International Job Applications
In many countries outside the US, a CV is the preferred document for all job applications. It’s often more detailed than a resume, and you may need to include information such as your date of birth and marital status. It’s always best to tailor your CV to the specific requirements of the country and the employer. Make sure to know the requirements of each country.
When to Use a Cover Letter
A cover letter is best used for most job applications, particularly in the United States. It’s a crucial part of the application process, providing a personalized introduction and highlighting your qualifications in relation to the specific job requirements. It helps you make a strong first impression and show how you fit the company’s needs. Use the cover letter to show enthusiasm about the job.
Job Applications (Especially in the US)

In the US, a cover letter is a vital part of your job application. It serves as an introduction, summarizing your skills and experiences, and highlighting how they align with the job requirements. Always tailor your cover letter to the specific job description, emphasizing your relevant accomplishments and your interest in the company. Your goal is to make it easy for the hiring manager to see how you fit the role.
Highlighting Specific Skills
Use your cover letter to highlight specific skills and experiences that are most relevant to the job. Select the experiences and skills that match the job description, and provide concise examples of how you’ve used these in the past. Tailoring your letter shows employers that you have taken the time to understand the role and are eager to demonstrate your suitability for the position. Always be sure to tailor it.
Tailoring to the Job
Customizing your cover letter to each job is key to making a strong impression. Research the company and the specific role, and then tailor your letter to match their needs. Highlight the skills and experiences that are most relevant, and explain how you can contribute to their success. This demonstrates that you are seriously interested in the position and have taken the time to understand the role and the company. Tailoring increases your chances of getting hired.
Tips for Writing Effective CVs and Cover Letters
CV Writing Tips
When writing your CV, focus on clarity, accuracy, and completeness. Use a clear and concise format, highlighting your key accomplishments and skills. Customize your CV to the specific job or opportunity whenever possible, emphasizing the information that’s most relevant. Always proofread your CV carefully to catch any errors in grammar or spelling. Use action verbs to describe your achievements. Always ensure your CV is up-to-date and reflects your current qualifications.
Cover Letter Writing Tips
For cover letters, start with a strong introduction that grabs the reader’s attention. Customize your letter to the specific job and company, demonstrating that you’ve done your research. Highlight your most relevant skills and experiences, and explain how you can contribute to the employer’s goals. End with a call to action, expressing your enthusiasm and your desire for an interview. Ensure your cover letter is well-written, free of errors, and shows your personality. Your cover letter should be personalized and professional.
Review and Proofreading
Before submitting your CV or cover letter, always review and proofread your documents carefully. Check for any errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Ensure that your formatting is consistent and that your contact information is accurate. Consider having a friend, colleague, or career counselor review your documents for feedback. Proofreading can prevent errors and ensures your professionalism. It makes all the difference.
Final Thoughts on CVs vs Cover Letters
Understanding the differences between a CV and a cover letter is vital for a successful job search. Choose the right document based on the requirements of the job application and the expectations of the employer. A well-crafted CV and cover letter will highlight your skills and experiences, setting you apart from other candidates. Tailor each document to the specific opportunity, always presenting yourself in the best possible light. With the correct use of both documents, you can increase your chances of landing your desired job.
